MongoDB Atlas
What is Mongo Atlas ?
Mongo Atlas is the cloud hosted version of MongoDB. This is the software-as-a-service flavor of the NoSQL database.
Why MongoDB Atlas ?
Since this is the software as a service and is hosted on the cloud it has several advantages over the on-premise hosted version:
-
Easy and quick ( in around 10-15 mins) to setup a production standard single replica set or sharded cluster of MongoDB.
-
Highly reliable cluster. The cluster is deployed on AWS (Amazon Web Service). Each member of the replica set is deployed on a different availability zone and thus providing a higher degree of fault tolerance for a particular replica set.
-
No need to have a NoSQl database management expertise.
-
Provides users the ability to configure backups of the database and also restore the data from backup when necessary.
-
Automated handling of failure scenarios. If the primary node goes down then Atlas automatically handles election of a new primary and recovery of the broken node.
-
Tracks various system level and database level metrics. These metrics are represented as graphs for users to drill down for a particular time frame and granularity.
-
Setup alerts based on different metrics and custom user set thresholds.
-
Pay as you go pricing. The pricing is dependent on your usage and the configuration you choose. This gives flexibility to organizations based on their use cases and financial capabilities.
Setting up a cluster
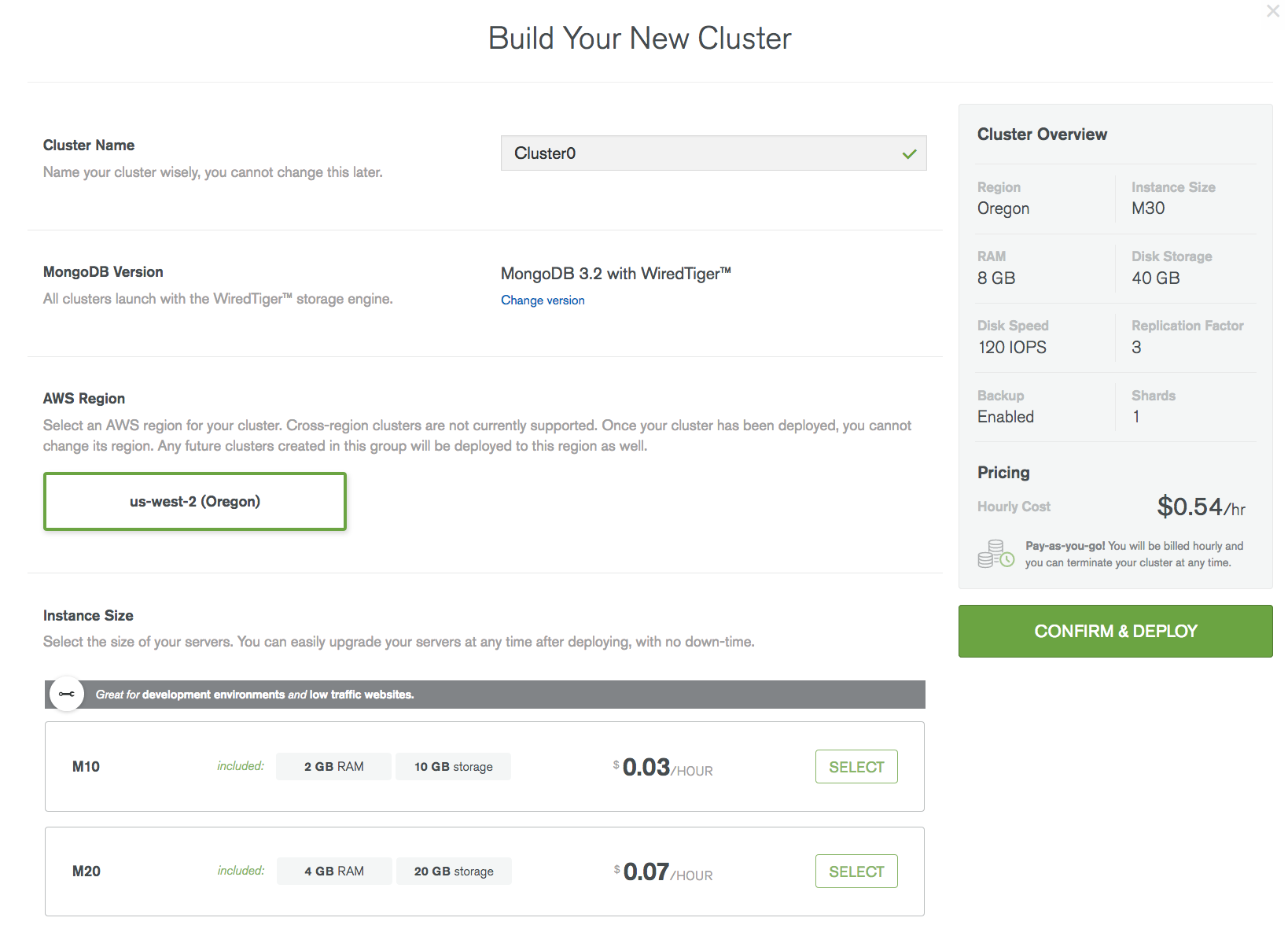
Once you have registered and created an account. You will be presented with a form where you can choose your desired configuration for the database.
The pricing displayed in the screenshots below are for the base minimum configuration. The price varies based on the choices you make for the below parameters.
To quickly give an overview of the choices you have
- The DB engine (3.2v WiredTiger or 3.4v WiredTiger). The older engine MMAP(memory mapped) is not supported in MongoDB Atlas.
- Right now the hosting is available only in the Oregon region of AWS.
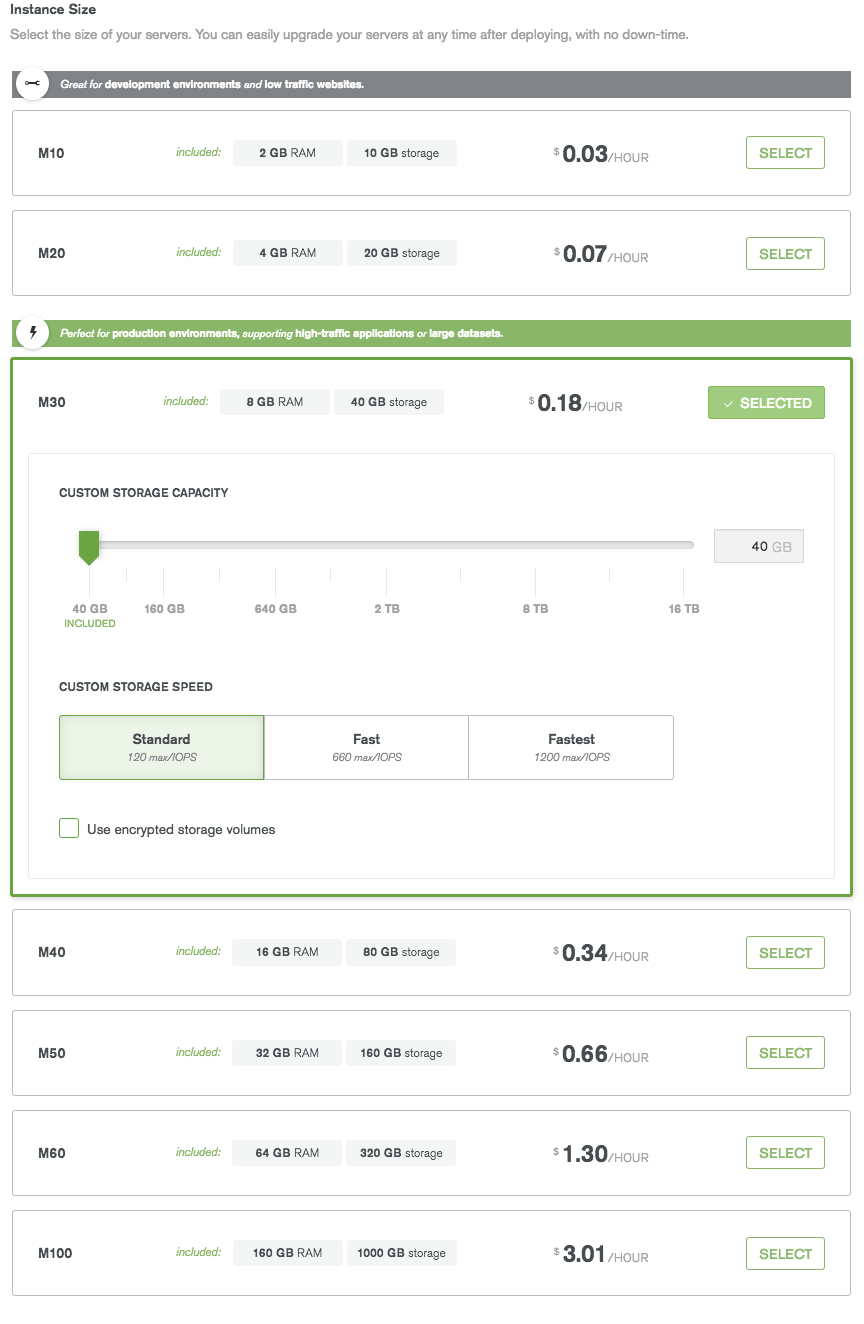
- The size of the instances on which to host the database. The instances need to be homogeneous. Different instances have different memory and CPU However, the storage can be configured as desired.
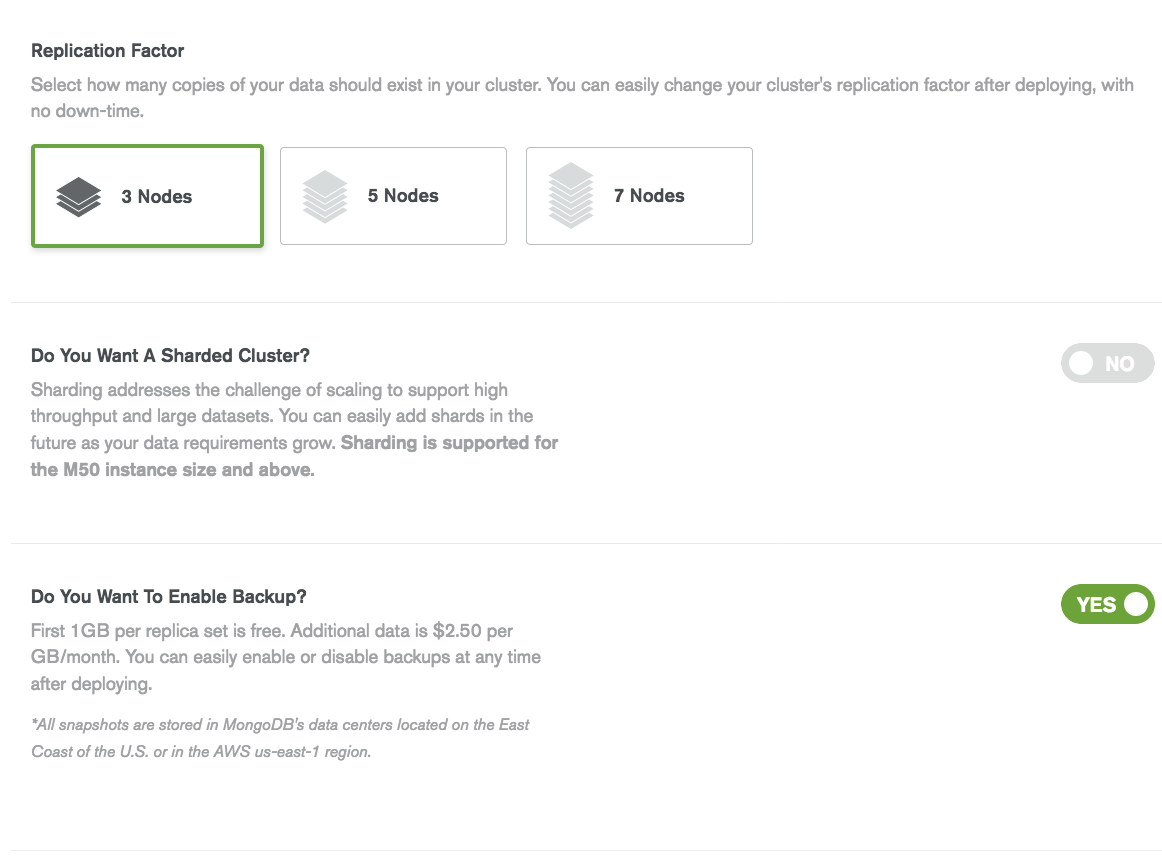
- Replication factor. Number of replica in a replica set.
- Whether to setup a single replica set stand-alone cluster or a sharded cluster.
- If the backup needs to be enabled or not.
 </img>
</img>
 </img>
</img>
 </img>
</img>
